The intramolecular Rh(I)-catalyzed
allenic Pauson-Khand reaction (APKR) is a powerful synthetic method for constructing ring-fused cyclopentenones. Our group's interest in the APKR extends back to 1992 when we submitted original research proposals for applications to academic positions. At that time, there were two independent reports of allenes being used in the PKR-only Aumann's demonstrated the feasibility of an
intermolecular Fe(0)-catalyzed process.
2a In 1994, Narasaka demonstrated three examples of an intramolecular APKR using
allenyl sulfides and an iron carbonyl complex.
3 In 1995, we reported a successful
intramolecular APKR reaction of
unfunctionalized allenes4 using stoichiometric Mo(CO)
6-a transition metal complex that had recently been reported by Jeong for the enyne PKR.
5 Also, in 1995, Narasaka reported trace amounts of a cycloadduct for a simple allene-yne using Fe(0)-catalysis,
6 and Cazes successfully demonstrated an
intermolecular APKR using Co
2(CO)
8 and NMO.
7 In July of 2000, an undergraduate researcher, Brenden Rickards, working in our lab demonstrated a Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR using [Rh(CO)
2Cl]
2-a catalyst previously reported by Narasaka for an
enyne PKR.
8 This result established for the first time that a Rh(I) transition metal catalyst afforded complete selectivity for the distal double bond of the allene whereas Mo(CO)
6 afforded selectivity for the proximal double bond affording a different constitutional isomer.
In 2001, while our group was expanding the scope of this unprecedented, catalyst-controlled double bond selectivity for Mo(0) and Rh(I) on a number of alkynyl allenes,
9a,b including an APKR approach to the natural product guanacastepene A,
9c Narasaka published a manuscript describing the scope and limitations of [Rh(CO)
2Cl]
2-catalyzed
enyne PKR where he also described the reaction of a single alkynyl allene showing that the reaction occurred with the distal double bond.
10 In early 2002, Dr. Hongfeng Chen, a postdoctoral fellow in our group, demonstrated that
unfunctionalized allenes could be used in the APKR to form [5,7]-ring systems by exploiting the Rh(I) catalyst controlled double bond selectivity,
9b and Mukai reported that
allenyl sulfones could also be employed to prepare [5,7]-ring systems.
11 This independent co-discovery of a metal catalyzed control of double bond selectivity to form seven-membered rings has inspired our group and others in the application of this powerful method for synthesizing complex molecular compounds.
This discussion addendum informs on a few recent advances made regarding expansion of the scope of the APKR and its application to target-oriented synthesis. We have divided this addendum into the following topics: Asymmetric Allenic Pauson-Khand Reaction; Transfer of Allene Axial Chirality in APKR; Rh(I)-Catalyzed APKR Double Bond Selectivity, Mechanism, and Reaction Optimization; and APKR Approach to Natural Products and Other Bioactive Compounds.
Asymmetric Allenic Pauson-Khand Reaction
Burrows, Jesikiewicz, Liu, and Brummond recently showed that through a combination of experiment and theory
racemic allene-yne
1 could be transformed to bicyclo[5.3.0]decadienone
2 in 79% yield with an 82:18 enantiomeric ratio (er) using a chiral non-racemic Rh(I) catalyst (Scheme 1A).
12 A transformation made possible through rapid scrambling of the axial chirality of the allenyl acetate under the reaction conditions and selective reaction of one enantiomer. This represents the first Rh(I)-catalyzed asymmetric carbocyclization reaction of this type outside of a 1,6-enyne. In contrast to more traditional catalyst design strategies involving high throughput experimentation, high enantioselectivity was realized after testing only seven different chiral catalysts using wet-lab experimentation-representing an immense savings in resources. The key to our success was a deep mechanistic understanding where experiment and computation informed selection of the next catalyst. For example, activation barriers for the enantioselectivity-determining oxidative cyclization step were computed to reveal the origins of catalyst reactivity (ΔG
‡) and selectivity (ΔΔG
‡) and experiments in a flask were performed to test catalyst efficiency (yield) and stereo-directing ability (er) (Scheme 1B). This mechanistically complex process involving a dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformation (DyKAT) is a powerful demonstration of catalyst design made possible through the tight integration of experiment and computation.
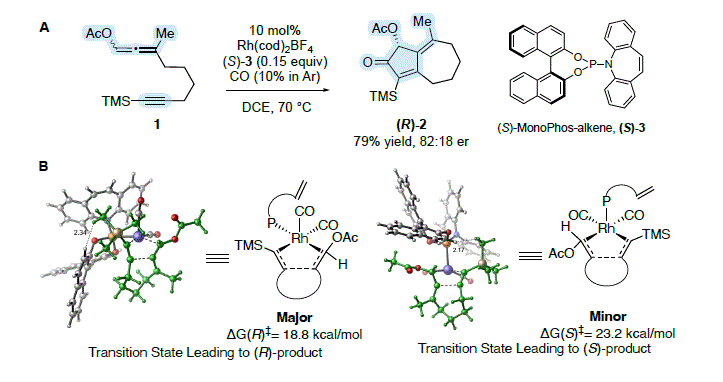
Scheme 1. DyKAT process realized in the asymmetric APKR
Deihl and Brummond expanded the asymmetric APKR to include furanyl tethered allene-ynes to access the core ring system present in the guaianolide natural product thapsigargin (Tg).
13 The APKR of several furanyl tethered allene-ynes
4 afforded products
5 in good yields with high enantioselectivities when using the chiral monodentate ligand
S-(
3) (Scheme 2). Interestingly, while several allenyl carboxy groups were examined (Series B), only allenyl chloroacetates afforded products in upwards of 98% ee (Series A)! The group on the terminus of the alkyne played a key factor in the yield and enantioselectivity of the APKR with a terminal alkyne affording product in 32% yield and 54% ee and a phenyl alkyne affording product in 46% yield and 98% ee. The methyl-substituted alkyne with an allenyl chloroacetate afforded product in 57% yield and 94% ee. DFT calculations of this reaction show a favorable π-π interaction between the furanyl ring and phosphoramidite ligand that lowers the energy of the transition state leading to the major product. The transition state leading to the minor enantiomer, lacks this favorable π-π interaction.
13
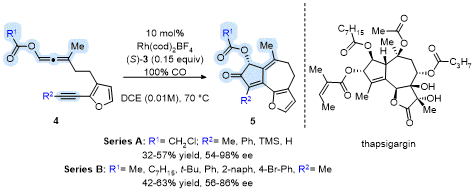
Scheme 2. APKR of furan-tethered allene-yne affording the Tg core
Transfer of Allene Axial Chirality in the APKR
The transfer of chiral information from the allene to the cyclocarbonylation product for the APKR of non-racemic allenes has also been demonstrated. Grillet and Brummond showed that reacting enantioenriched
1,3,3-trisubstituted allenes
6 and
8 to the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR afforded bicyclo[5.3.0]decadienone products
7 and
9 with complete transfer of chiral information for 17 substrates (Scheme 3A).
14 Success was realized for allene-ynes having variety of groups on the alkyne terminus (Me, Ph, H, TMS, 2-, 3-thiophenyl, cyclopropyl), allene (Ph, Me, n-Bu, SiMe
2Ph), and tether (X = NTs, C(CO
2Et)
2,O). In the case of
1,3-disubstituted allenes, the degree of chirality transferred depended upon the tether identity and the alkynyl group (Scheme 3B). For example, allene-yne
10a (X = NTs, R= TMS) afforded
11a in 83% yield in 84% ee, whereas allene-yne
10b (X = C(CO
2Et)
2, R= TMS) and
10c (X = O, R= TMS) provided the products
11b and
11c in good yield but with 50% and 22% ee, respectively. Reaction monitoring using chiral HPLC analysis provided strong evidence for scrambling of the axial chirality of the allenyl precursor and not epimerization of the APKR product. Scrambling of the axial chirality of the allene is postulated to involve an intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the rhodium complexed allene by the heteroatom in the tether (Scheme 3C).
14
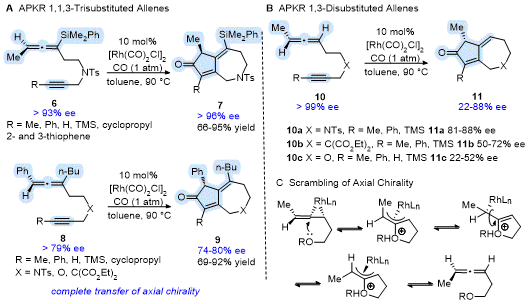
Scheme 3. Transfer of allene axial chirality in the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR to access bicyclo[5.3.0]decadienones enantioselectively
Ma and coworkers have shown that chiral non-racemic 1,3-disubstituted allenes
12 afford bicyclo[4.3.0]nonadienones
13 with complete transfer of chirality (Scheme 4).
15 Low reaction temperatures and silver salt additives were critical to the success of the preferred mechanistic pathway affording the cyclocarbonylation product. Higher temperatures in the absence of silver hexafluoroantimonate afforded the corresponding cross conjugated triene via a formal Alder-ene process. High yields and enantiospecificities were reported for the APKR of ten allene-ynes.
Scheme 4. Transfer of allene axial chirality in the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR to access chiral non-racemic bicyclo[4.3.0]nonadienones
Rh(I)-Catalyzed APKR Double Bond Selectivity, Mechanism, and Reaction Optimization
Rhodium and molybdenum are the most used transition metals for catalyzing the
intramolecular APKR with each showing a different reactivity preference towards the double bonds of the allene. For example, rhodium biscarbonyl chloride dimer [Rh(CO)
2Cl]
2 reacts preferentially with the distal double bond of the allenes
14 and
17 to afford products
15 and
18, while molybdenum hexacarbonyl [Mo(CO)
6] reacts with the proximal double bond to afford
16 and
19. This transition metal controlled selectivity has been used to form either α-methylene cyclopentenone or 4-alkylidene cyclopentenone products (Scheme 5).
9a,bScheme 5. Catalyst-controlled double bond selectivity for APKR
The preferential reactivity of one double bond over the other has been described using Density Functional Theory (DFT) where calculations show the
metal geometry in the oxidative cyclization (OxCycl) transition state-
the rate determining step in the reaction energy profile-as a key control element.
16 For example, the rhodium catalyzed reaction shows an early transition state (TS) with all low energy TS structures for the OxCycl step having a four-coordinate rhodium metal complexed to the distal allene double bond (
TS-1) and adopting a slightly distorted square planar geometry to afford metallocycle
22 (Scheme 6A). Whereas all low energy TS structures for the OxCycl step for the five-coordinate molybdenum having a trigonal bipyramidal geometry show the proximal double bond as complexing to the axial position due to conformational constraints (not shown) The CO insertion step was found to be the rate-determining step for molybdenum; however, the free energy of this step was lower than that for the OxCycl of the metal to the distal double bond of the allene (not shown).
16
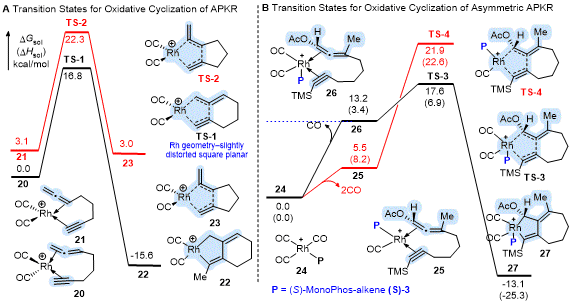
Scheme 6. DFT studies on the oxidative cyclization step of the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR and asymmetric APKR
The computed reaction energy profile for the asymmetric Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR shows the oxidative cyclization step as stereo- but not rate-determining (Scheme 6B).
12 Complexation of the allene-yne to the resting state of the catalyst
24 occurs with the loss of two CO's to afford
25 having a square planar geometry which is 7.7 kcal/mol lower in energy than the square-based pyramidal complex
26, which results from the loss of one CO (Scheme 6B). Nonetheless, the OxCycl step for the five-coordinate
TS-3 has a lower calculated activation barrier than the four-coordinate
TS-4 by 4.3 kcal/mol. Stabilization of
TS-3 (18-electron) over
TS-4 (16-electron) by the additional CO ligand was attributed to the acetoxy group on the allene. Interestingly, DFT predicts that both reaction pathways afford the same enantiomeric product. Whereas, in the Rh(I)-catalyzed PKR of enynes, the reaction pathways involving the four- and five-coordinate complexes afford different enantiomeric products.
17During application of the APKR involving an early-stage installation of C4 and C10 methyl groups present in the 6,12-guaianolides, a byproduct was formed in substantial quantities for methyl substituted allenes and alkynes as well as terminal alkynes.
1H NMR spectroscopy and ESI mass spectrometry analysis supported a byproduct resulting from a dimerization of the allene-yne precursor
28. Performing the reaction by dropwise addition of allene-ynes
28 to the Rh(I) catalyst under Conditions B (0.01 M) gave an 80% yield of
29, much higher than Conditions A which afforded
29 in 32% yield
. High yields were afforded for nearly all substrates examined when using these modified conditions (Scheme 7).
18 These same conditions were used for APKR protocol published in Organic Syntheses on a 6-g scale in 88% yield using 1 mol% of [Rh(CO)
2Cl]
2.
19Scheme 7. Optimized conditions for Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR
APKR Approach to Natural Products and Other Bioactive Compounds
The APKR is a key step in the synthesis of the core structure of several natural products and other bioactive compounds. Jackson and Brummond demonstrated that the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR of lactam tethered allene-ynes
32 enabled rapid access to several guaianolide analogs
33, which are equipped with an electronically tunable covalent reactive group, an α-methylene−γ-lactam (Scheme 8A).
20 These analogs were designed for tunable thiol reactivity thus enabling an understanding of structure activity relationships for bioactive compounds with an α-methylene−γ-lactone that are otherwise too reactive. Reaction of compound
33 with excess cysteamine showed thiol addition with half-lives ranging from seconds to days depending upon the electronics of the R
2 group.
Scheme 8. APKR approach to guaianolide analogs with tunable thiol reactivity and bioactivity
Dempe and Brummond have shown that reaction of cis and trans-annulated lactams
35 to the Rh(I) conditions afforded APKR products
36 in yields ranging from 47-85% (Scheme 8B). Reaction times for the APKR varied considerably across this series of lactams with the trans-allene-ynes reacting 2-4× faster than the cis-isomers. Furthermore, lactam
36 reacted with excess glutathione 10x faster than cis-annulated lactams under biologically relevant conditions (Scheme 8B).
21 DFT calculations revealed this higher reactivity of the trans-annulated stereoisomer is due to release of ring strain in the thiol-Michael addition transition state. These studies support the α-methylene-γ-lactam as a novel covalent reactive group and its value in the rational design of inhibitors by having thiol reactivity within a range of the widely used and therapeutically proven acrylamide.
21,22In 2022, the Li group reported the first use of APKR of an unfunctionalized allene
38 to form an eight-membered-ring to achieve the asymmetric total synthesis of hypoestin A, albolic acid, and ceroplastol II from the common intermediate
40 (Scheme 9).
23,24 Several rhodium catalysts and additives were screened identifying the standard APKR conditions ([(Rh(CO)
2Cl]
2, toluene, CO balloon, 110 °C) as optimal for achieving the 5,8,5-ring system
39 in 56% yield. The APKR could be performed reliably on a 2-g scale and the generality of the method was demonstrated on ten additional substrates with various functionality affording 5,8,5-ring systems in 40-86% yields.
Scheme 9. APKR approach to a 5,8,5-ring system
In 2021, the Poulsen group reported an APKR on an allene-ynamide
41 to deliver the azabicyclo[4.3.0] core
42 via reaction with the distal double bond of the allene in 66% yield. This reaction was performed on a gram-scale using either a constant flow of CO (10% CO mixed with 90% argon) or COgen-a bench stable CO precursor-in a two-chamber system to generate carbon monoxide in situ. Compound
42 was taken on to afford concise syntheses of streptazone A, and abikoviromycin (Scheme 10).
25Scheme 10. APKR approach to 5,6-ring system-Total synthesis of streptazone A and abikoviromycin
The Li group used an APKR of benzyloxyallene-yne
43 to construct the 5,7,6,5- tetracyclic ring system
44 in the total synthesis of sterically compact bufospirostenin A (Scheme 11).
26 Extensive experimentation revealed that the ligand additive 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) and the syringe pump addition of allene-yne to the rhodium catalyst afforded the desired product in 85% yield as a 2:1 mixture of diastereomers separable by column chromatography on large scale (>20 g).
Scheme 11. APKR approach to 5,7,6,5-ring system
In 2017, the Grenning group combined a deconjugative propargylation and a Cope rearrangement to afford
45, which was reacted to the Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR to rapidly assemble the 6,7,5-ring system of
46-a terpenoid core represented in several natural products including brevifoliol and radianspene C (Scheme 12).
27Scheme 12. Rapid assembly of 6,7,5-ring system of a terpenoid core
The Yang group reported using ene-allene
47 in a Rh(I)-catalyzed cyclocarbonylation reaction to from a tricyclic core
48 as a single isomer that was used to complete the total synthesis of perforanoid A (Scheme 13).
28 The use of an ene-allene in this transformation was the result of an alkyne isomerization prior to the cyclocarbonylation which ultimately afforded the desired product as that of an enyne due to isomerization of the double bond into conjugation with the ketone. While not technically an APKR, the high yielding cyclocarbonylation of ene-allene
47 demonstrates the extraordinary scope, and potential, of the Rh(I)-catalysis conditions.
Scheme 13. Cyclocarbonylation of ene-allene
Baran and coworkers have demonstrated the APKR of allene-yne
49 to prepare
50 which was used in the total syntheses of ingenol and phorbol (Scheme 14).
29, 30 Protection of the diol as silyl ethers, high temperature, and high dilution conditions were essential to this high yielding APKR on gram scale.
Scheme 14. APKR approach to a 5,7-ring system
Ardisson and coworkers have shown that a Rh(I)-catalyzed APKR performed using racemic allene-yne
51 affords the 5,7-ring system of the tricyclic
52 in 71% yield in an approach to the natural product thapsigargin (Scheme 15).
31 The structure of
52 was confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The APKR conditions were modified to include 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp). These conditions have previously been demonstrated to give a dramatic yield enhancement for some allene-ynes, including: allenyl carbamates, and benzyl and para-methoxy benzyl ethers. Interestingly, the catalyst and ligand were added successively to the allene-yne whereas most protocols involve the addition of the allene-yne to the Rh(I)-catalyst.
32, 33Scheme 15. APKR approach to a 5,7-ring system of thapsigargin
In summary, the APKR has played an important role in target-oriented organic synthesis. And, amongst different metals including Fe, Mo, and Co being used as the catalyst in APKR, Rh is the most prominent in the recent advances in this area. Finally, for additional insight and information on the APKR several reviews have been published.
34
Copyright © 1921-, Organic Syntheses, Inc. All Rights Reserved