Checked by Tohru Fukuyama and Takuya Nishimura.
1. Procedure
2. Notes
1.
THF 99.9+% was purchased from Kanto Chemicals Co., Inc., and was purified using a Glass Contour Solvent System; The submitters purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. and processed through a Solvent Purification System (M. Braun SPS-800, filter material: MB-KOL-A, MB-KOL-M; catalyst: MB-KOL-C).
2.
Granular
lithium, 99.9+%, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. and was used as received.
3.
α,α'-Dibromo-o-xylene, 96%, was purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc. and was sublimed in a Kugelrohr distillation apparatus, which was equipped according to
Note 11 (air bath temperature 130-150 °C, 0.07 mmHg) yielding white crystals, which were rinsed out of the receiver flask with diethyl ether. The solvent was removed via rotary evaporation and the residual colorless crystals were dried under vacuo for 2 h (25 °C, 0.04 mmHg). Upon use of α,α'-dibromo-
o-xylene as purchased, i. e. without purification, the yield of
1 dropped to 44-46%, and the submitters have experienced problems with drying the crude product before purification by Kugelrohr distillation.
4.
The addition of α,α'-dibromo-
o-xylene may cause a rapid rise of temperature. The addition may need to be temporarily suspended upon onset of the exothermic reaction.
5.
The TLC analysis was performed on Merck precoated analytical plates, 0.25 mm thick, silica gel 60 F
254and PE as eluent; detection: UV-light (254 nm) or aqueous KMnO
4 (1% KMnO
4 + 5% Na
2CO
3 in H
2O), R
f (α,α'-dibromo-
o-xylene)
= 0.21, R
f (
1)
= 0.18, R
f (
4) = 0.12
(Note 7).
6.
The submitters also monitored the reaction by the GC/MS analysis with a Hewlett-Packard 5890 Series II gas chromatograph equipped with a 5972 series mass selective detector and a HP-1 column (25 m × 0.2 µm; 0.33 mm film thickness, carrier gas: helium). For reaction control the following parameters were used; temperature-program: 50 °C for 3 min; heating rate 20 °C/min; 250 °C for 10 min; injection-temperature 250 °C). GC/MS (EI): t
R(α,α'-dibromo-
o-xylene) = 8.9 min,
m/z = 264 [M
+]; t
R(
1) = 10.9 min,
m/z 208 [M
+]; t
R(
4) = 11.5 min,
m/z = 312 [M
+].
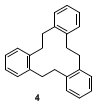
7.
The by-product 5,6,11,12,17,18-hexahydro-tribenzo[a,e,i]cyclodo-decene (
4) was identified by the following data: mp = 184-185 °C (lit.,
2 184.5 °C);
1H NMR
(CDCl
3, 300.13 MHz) d: 3.04 (s, 12 H, CH
2), 7.20-7.36 (m, 12 H, Aryl);
13C NMR (CDCl
3, 75.48 MHz) d: 37.45 (t, CH
2), 126.87, 130.61 (2 d, C-Ar), 140.22 (s, C
quart.-Ar); IR (KBr): 3058, 3011, 2939, 2864, 1913, 1489, 1473, 1450, 1158, 1051, 1040 cm
-1; HRMS: Calcd. for C
24H
24: 312.1878. Found: 312.1888; MS (EI, 70 eV):
m/z (%): 312 (40), 207 (100), 193 (30), 178 (30), 115 (40), 105 (35), 91 (25), 78 (25).
8.
At ca. 75 mmHg a white solid precipitates.
10.
Silica gel (0.04-0.100 mm) was purchased from Kanto Chemical.
11.
Purification by Kugelrohr distillation was carried out in an apparatus equipped with a straight oven tube (29 mm neck fit and 20 cm length) and a cooled 100-mL single bulb receiver flask. A high vacuum pump was used to reduce the pressure. The submitters reported that fraction 1 (130-160 °C, 0.08-0.05 mmHg) yielded 17.3 g of
1, fraction 2 (160-180 °C, 0.05 mmHg) yielded 4.2 g of
1 and the triple-coupled by-product
4 as a mixture and fraction 3 (185-250 °C, 0.06 mmHg) yielded 3.8 g of
4 as a pale brown solid. Fraction 2 was subjected to Kugelrohr distillation again to yield 3.3 g of pure
1. On a smaller scale run (6.6 g, 25 mmol, of α,α'-dibromo-
o-xylene)
1 and
4 were isolated via chromatography on a column (2.5 x 50 cm) of 70 g silica gel with petroleum ether (35-60 °C) as eluent. The product
1 was obtained in fractions 5-15 (100-mL fractions) and
4 in fractions 20-33. After evaporation of the solvent by rotary evaporation (40 °C, 262 mmHg)
1 was obtained as colorless plate shaped crystals (1.09 g, 42%) and the by-product
4 as colorless needles (0.14 g, 6%).
12.
Compound
1 has the following physicochemical properties: mp = 108-109 °C (lit.
10 mp 108.5-110 °C);
1H NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 400 MHz) δ: 3.06 (s, 8 H, CH
2), 6.99 (s, 8 H, Aryl-H);
13C NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 100 MHz) δ: 35.12 (t, CH
2), 126.07, 129.64 (d, C-Ar), 140.57 (s, C
quart.-Ar); IR (KBr): 3060, 3011, 2939, 2899, 2845, 2359, 1914, 1491, 1476, 1450, 1157, 1079, 1050.cm
-1; Anal. Calcd. for C
16H
16: C, 92.26; H, 7.74. Found: C, 92.18; H, 7.87. HRMS: Calcd. for C
16H
17: 209.1330. Found: 209.1321; MS (EI, 70 eV):
m/z (%): 208 (54), 193 (100), 178 (40), 165 (11), 152 (5), 130 (7), 116 (24), 104 (29), 91 (13), 78 (27).
13.
Carbon tetrachloride (99%, extra pure) was purchased from Kanto Chemical and was used as received.
14.
NBS, 99%, purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc was used as received.
15.
The use of 2.15 equiv of NBS was necessary for the complete consumption of the substrate. With only 2.0 equiv of NBS the product was obtained as a mixture of undesired monobrominated product and desired product
2 in a ratio of 14/86, which was determined via its proton
NMR spectrum.
16.
Analysis via TLC monitoring was unsuccessful, because the R
f values of the dibrominated product
2 and the monobrominated intermediate are the same. Therefore, even if the spot of
1 has disappeared and only the spot of the dibrominated product
2 is visible, conversion might still be incomplete.
17.
NMR analysis was conducted in the following manner; a portion of reaction mixture (approximately 10-15 μl) was removed by Pasteur pipette or capillary and dissolved in CDCl
3. Completion of the reaction was confirmed by disappearance of monobrominated intermediate peaks found in the
1H NMR (400 MHz) spectrum at d = 3.04 (s), 3.06 (s), 3.48-3.76 (m), 3.96 (dd,
J = 11.0, 14.2 Hz). The submitters monitored the reaction by GC/MS, For reaction control the "default"-method was used (see
Note 6). GC/MS (EI): t
R(succinimide) = 5.9 min,
m/z = 99 [M
+]; t
R(
1) = 10.9 min,
m/z 208 [M
+]; t
R(monobrominated intermediate) = 12.5 min,
m/z = 286 [M
+]; t
R(
2) = 14.8 min,
m/z = 366 [M
+].
18.
The yield of crude product was significantly lower if the solution was filtered after allowing it to cool to room temperature.
19.
Compound
2 was used in the next step without further purification. The compound can, however, be purified by recrystallization: The solid (3.0 g) is dissolved in 12 mL of hot carbon tetrachloride at 85 °C (oil bath temperature). The yellow solution is allowed to cool slowly to room temperature by turning off the heating of the oil bath. Then the flask is cooled to 6 °C (refrigerator) overnight, and the resulting crystals are collected by suction filtration through a small Büchner funnel (diameter 2 cm), washed with 4 mL of ice-cold dichloromethane, and then dried under vacuum (0.04 mmHg, 14 h) to provide 1.3 g of
2 as colorless rods with the following physicochemical properties: mp = 188-189 °C (lit.
10 mp 188-189 °C);
1H NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 400 MHz) δ: 3.65 (dd,
J = 8.2, 14.2 Hz, 2 H), 4.29 (dd,
J = 11.0, 14.2 Hz, 2 H), 5.33 (dd,
J = 11.0, 8.2 Hz, 2 H), 6.95-7.11 (m, 8 H, Ar-H)
13C NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 100 MHz) δ: 43.65 (d, C-2), 52.98 (s, C-1), 127.88, 129.03, 130.78, 130.92 (4 d, C-Ar), 136.32, 138.33 (2 s, C
quart.); IR (KBr): 3062, 3018, 2892, 1961, 1600, 1579, 1490, 1449, 1312, 1110, 1084 cm
-1; Anal. Calcd. for C
16H
14Br
2: C, 52.49; H, 3.85; Br, 43.65. Found: C, 52.37; H, 4.03; Br, 43.72. HRMS: Calcd. for C
16H
1479Br
81Br: 365.9442. Found: 365.9457; MS (EI, 70 eV): 287 (22), 285 (23), 205 (100), 191 (20), 178 (15), 165 (10), 115 (11), 101 (16), 89 (23).
20.
Potassium
tert-butoxide (97%) was purchased from Fluka, stored in a Schlenk flask under argon and was used as received.
21.
The TLC analysis was carried out according to
Note 5, R
f (
2) = 0.11, R
f (
3) = 0.20.
22.
The submitters also monitored reaction by GC/MS. For GC/MS-control the "default"-method was used (see
Note 6). GC/MS (EI): t
R(
3) = 10.9 min,
m/z = 204 [M
+]; t
R(
2) = 14.8 min,
m/z = 366 [M
+].
23.
If after rotary evaporation the crude product remains as a semifluid mass and cannot be scraped off the inner walls of the flask, it is dissolved in diethyl ether and the solvent is evaporated once more.
24.
Kugelrohr distillation was carried out in an apparatus equipped according to
Note 11. The first fraction, up to 85 °C, is
tert-butanol.
25.
From a smaller scale run (0.62 g, 2.98 mmol of
1)
3 was isolated via chromatography on a column (3.0 x 15 cm) of 25 g silica gel with petroleum ether (35-60 °C) as eluent. The desired product
3 was obtained in fractions 2-3 (50-mL fractions), which were concentrated by rotary evaporation (40 °C, 262 mmHg) to yield
3 as colorless plates (0.44 g, 72% over two steps).
26.
Physicochemical properties of dibenzo[a,e]cyclooctene
3: mp 108-109 °C (lit.
10 109.5-110 °C);
1H NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 300.13 MHz) δ: 6.72 (s, 4 H, CH), 7.02-7.11 (m, 8 H, Ar-H);
13C NMR
pdf (CDCl
3, 100 MHz) δ: 126.76 (d, CH), 129.03, 133.18 (2 d, C-Ar), 137.00 (s, C
quart.-Ar); IR (KBr): 3054, 3010, 1922, 1815, 1650, 1490, 1432, 1400, 1153, 1088, 1039 cm
-1; Anal. Calcd. for C
16H
12: C, 94.08; H, 5.92. Found C, 94.14; H, 6.14. HRMS: Calcd. for C
16H
13: 205.1017. Found: 205.1017. MS (EI, 70 eV): 204 (79), 203 (100), 202 (63), 176 (5); 150 (4), 101 (30), 88 (10), 76 (7).
The procedures in this article are intended for use only by persons with prior training in experimental organic chemistry. All hazardous materials should be handled using the standard procedures for work with chemicals described in references such as "Prudent Practices in the Laboratory" (The National Academies Press, Washington, D.C., 2011 www.nap.edu). All chemical waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. For general guidelines for the management of chemical waste, see Chapter 8 of Prudent Practices.
These procedures must be conducted at one's own risk. Organic Syntheses, Inc., its Editors, and its Board of Directors do not warrant or guarantee the safety of individuals using these procedures and hereby disclaim any liability for any injuries or damages claimed to have resulted from or related in any way to the procedures herein.
3. Discussion
Appendix
Chemical Abstracts Nomenclature (Collective Index Number);
(Registry Number)
5,6,11,12-Tetrahydrodibenzo[a,e]cyclooctene; (1460-59-9)
α,α'-Dibromo-o-xylene, 1,2-Bis(bromomethyl)benzene; (91-13-4)
Tetrahydrofuran; (109-99-9)
Lithium; (7439-93-2)
5,6,11,12,17,18-Hexahydro-tribenzo[a,e,i]cyclododecene; (4730-57-8)
5,11-Dibromo-5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[a,e]-cyclooctene; (94275-22-6)
N-Bromosuccinimide; (128-08-5)
Carbon tetrachloride; (56-23-5)
Dibenzo[a,e]cyclooctene; (262-89-5)
Potassium tert-butoxide; (865
-47-4)
Copyright © 1921-, Organic Syntheses, Inc. All Rights Reserved